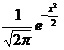 , Df = R, Wf = (0; 1/√(2π)], reelle Funktion, Funktion achsensymmetrisch zur Senkrechten x = 0, x -> -∞: f(x) -> -∞, x -> +∞: f(x) -> 0 = y als Grenzkurve ->
, Df = R, Wf = (0; 1/√(2π)], reelle Funktion, Funktion achsensymmetrisch zur Senkrechten x = 0, x -> -∞: f(x) -> -∞, x -> +∞: f(x) -> 0 = y als Grenzkurve ->www.michael-buhlmann.de
Funktion: f(x) = 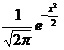 , Df = R, Wf = (0; 1/√(2π)], reelle Funktion, Funktion achsensymmetrisch zur Senkrechten x = 0, x -> -∞: f(x) -> -∞, x -> +∞: f(x) -> 0 = y als Grenzkurve ->
, Df = R, Wf = (0; 1/√(2π)], reelle Funktion, Funktion achsensymmetrisch zur Senkrechten x = 0, x -> -∞: f(x) -> -∞, x -> +∞: f(x) -> 0 = y als Grenzkurve ->
| Wertetabelle: | |||||
| x | f(x) | f'(x) | f''(x) | f'''(x) | Besondere Kurvenpunkte |
| -5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| -4.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| -4 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | |
| -3.5 | 0.0009 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| -3 | 0.0044 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.08 | |
| -2.5 | 0.0175 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.14 | |
| -2 | 0.054 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.11 | |
| -1.5 | 0.1295 | 0.19 | 0.16 | -0.15 | |
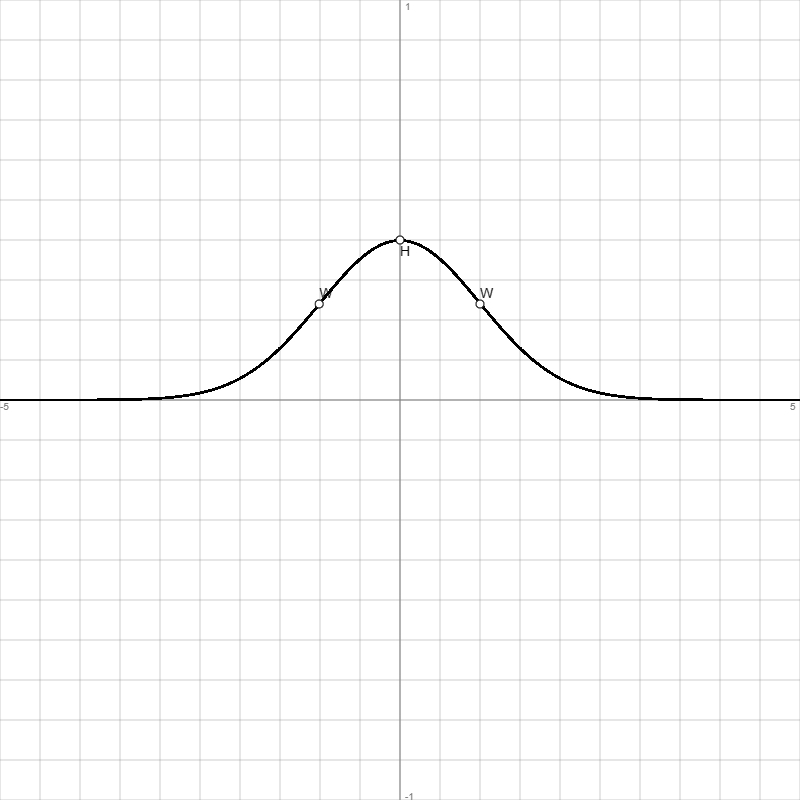
| -1 | 0.242 | 0.24 | 0 | -0.48 | Wendepunkt W(-1|0.24) |
| -0.5 | 0.3521 | 0.18 | -0.26 | -0.48 | |
| 0 | 0.3989 | 0 | -0.4 | 0 | Schnittpunkt Sy(0|0.4) = Hochpunkt H(0|0.4) |
| 0.5 | 0.3521 | -0.18 | -0.26 | 0.49 | |
| 1 | 0.242 | -0.24 | 0 | 0.48 | Wendepunkt W(1|0.24) |
| 1.5 | 0.1295 | -0.19 | 0.16 | 0.14 | |
| 2 | 0.054 | -0.11 | 0.16 | -0.11 | |
| 2.5 | 0.0175 | -0.04 | 0.09 | -0.14 | |
| 3 | 0.0044 | -0.01 | 0.04 | -0.08 | |
| 3.5 | 0.0009 | 0 | 0.01 | -0.03 | |
| 4 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0 | -0.01 | |
| 4.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Graph: | |||||
 | |||||
Abkürzungen: Df = (maximaler) Definitionsbereich, f(x) = Funktion, f'(x) = 1. Ableitung, f''(x) = 2. Ableitung, f'''(x) = 3. Ableitung, H = Hochpunkt, L = Lücke, N = Nullstelle, P = Polstelle, R = reelle Zahlen, S = Sprungstelle, T = Tiefpunkt, W = Wendepunkt, WS = Sattelpunkt, Wf = Wertebereich, {.} = ein-/mehrelementige Menge, [.; .] = abgeschlossenes Intervall, (.; .) = offenes Intervall, [.; .), (.; .] = halboffenes Intervall, ∞ = unendlich.
Bearbeiter: Michael Buhlmann