|
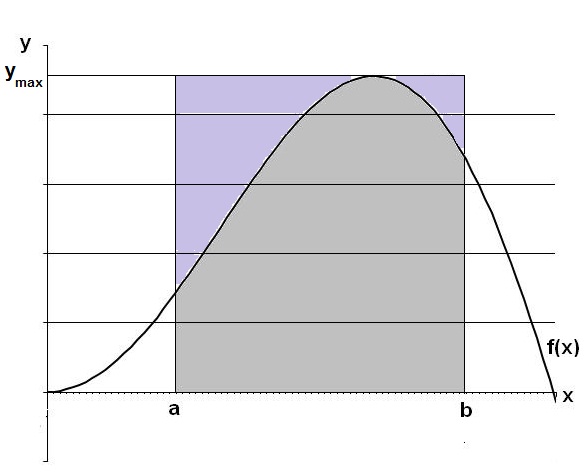
Monte-Carlo-Verfahren zur Bestimmung der Fläche zwischen einer Funktion f(x)≥0 und der x-Achse auf einem Intervall [a; b]
-> A = a∫b f(x) dx = AR*nTreffer/n mit AR = (b-a)*ymax, ymax = max{f(x)|x∈[a,b]}, nTreffer = Anzahl der Zufallspunkte P(x|y) zwischen Funktion und x-Achse,
n = Anzahl der insgesamt erzeugten Zufallspunkte.
Funktionseingabe (gemäß JavaScript): Variable x, Klammern (), Addition +, Subtraktion -, Multiplikation *, Division /,
Betrag |x| = Math.abs(x), Potenzfunktion xn = Math.pow(x,n), Wurzelfunktion √x = Math.sqrt(x), Exponentialfunktion ex = Math.exp(x), natürlicher Logarithmus ln(x) = Math.log(x),
trigonometrische Funktionen sin(x) = Math.sin(x), cos(x) = Math.cos(x), tan(x) = Math.tan(x), trigonometrische Umkehrfunktionen arcsin(x) = Math.asin(x), arccos(x) = Math.acos(x), arctan(x) = Math.atan(x).
|
 |
