Lage Punkt-Ebene: Punktprobe, Abstand
|
Abbildung: |
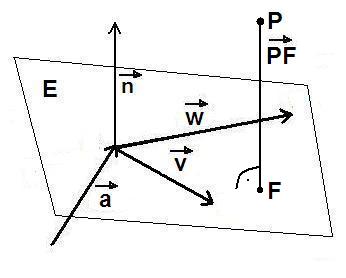 |
Eingabe der x1-, x2- und x3-Koordinaten des Punktes bzw. der Ebene in Parameter-, Normalen- oder Koordinatenform (bei Dezimalzahlen Punkt statt Komma):
www.michael-
buhlmann.de
|
Abbildung: |
 |
Eingabe der x1-, x2- und x3-Koordinaten des Punktes bzw. der Ebene in Parameter-, Normalen- oder Koordinatenform (bei Dezimalzahlen Punkt statt Komma):